Introduction
In the fast-paced and highly competitive arena of financial markets, traders are constantly on the lookout for any advantage they can find. Among the multitude of tools and strategies available, one concept stands out as particularly powerful: empirical regularity. Empirical regularities represent consistent patterns or relationships observed in historical market data. They serve as the cornerstone upon which trading strategies are built, offering traders invaluable insights into market dynamics and potential future price movements. This article delves into the intricacies of empirical regularity in trading, exploring its significance, applications, and challenges in today’s dynamic financial landscape.
Understanding Empirical Regularity
Empirical regularity in trading refers to the consistent patterns and relationships observed in historical market data. These patterns may manifest across various timeframes, assets, and market conditions, providing traders with valuable clues about potential future price movements. The concept is grounded in the idea that market behavior is not entirely random but rather governed by underlying principles and dynamics. By identifying and understanding these empirical regularities, traders can gain a deeper insight into market mechanics and develop more effective trading strategies.
Empirical regularities can take many forms, ranging from simple price action patterns to complex intermarket relationships. Some common examples include trend formations, price reversals, volatility cycles, and correlations between different asset classes. These regularities are often identified through rigorous data analysis techniques, such as statistical analysis, machine learning algorithms, and data visualization tools. By meticulously examining historical price charts, volume data, and other relevant indicators, traders can uncover recurring patterns and relationships that inform their trading decisions.
Leveraging Empirical Regularities in Trading Strategies
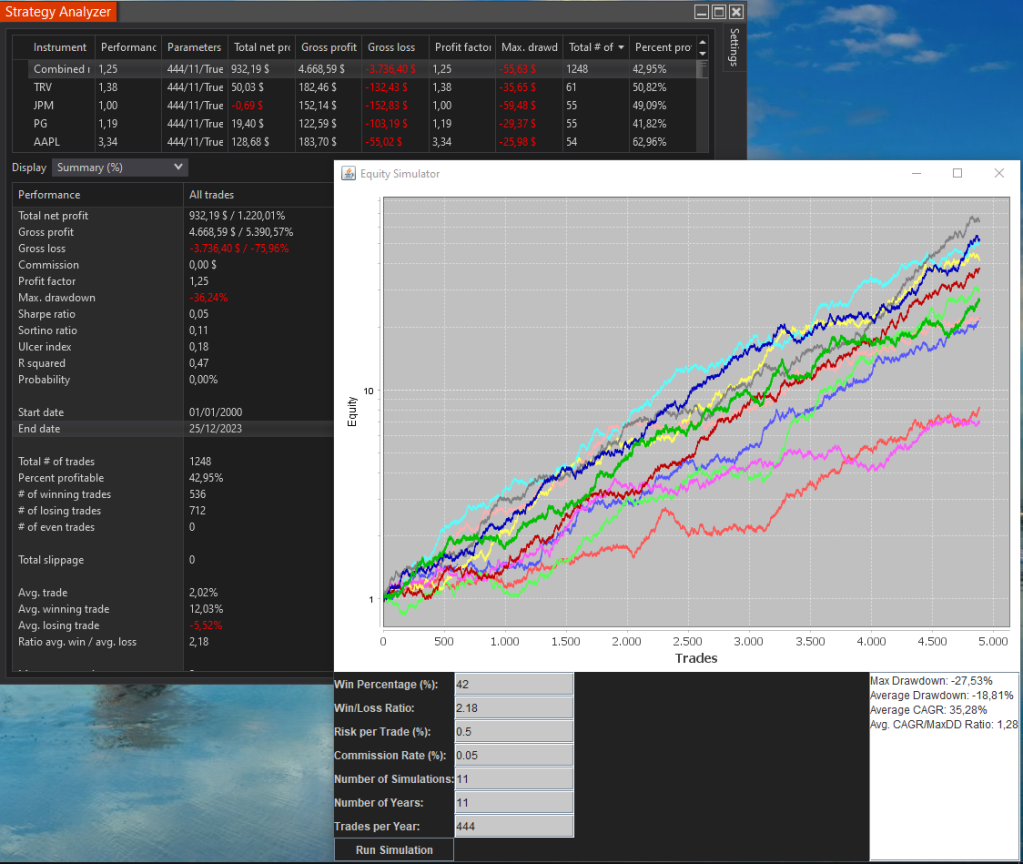
Empirical regularities serve as the foundation upon which trading strategies are built. Armed with insights gleaned from historical data analysis, traders can develop robust strategies that capitalize on recurring market patterns. These strategies can be broadly categorized into two main approaches: trend-following and mean-reversion.
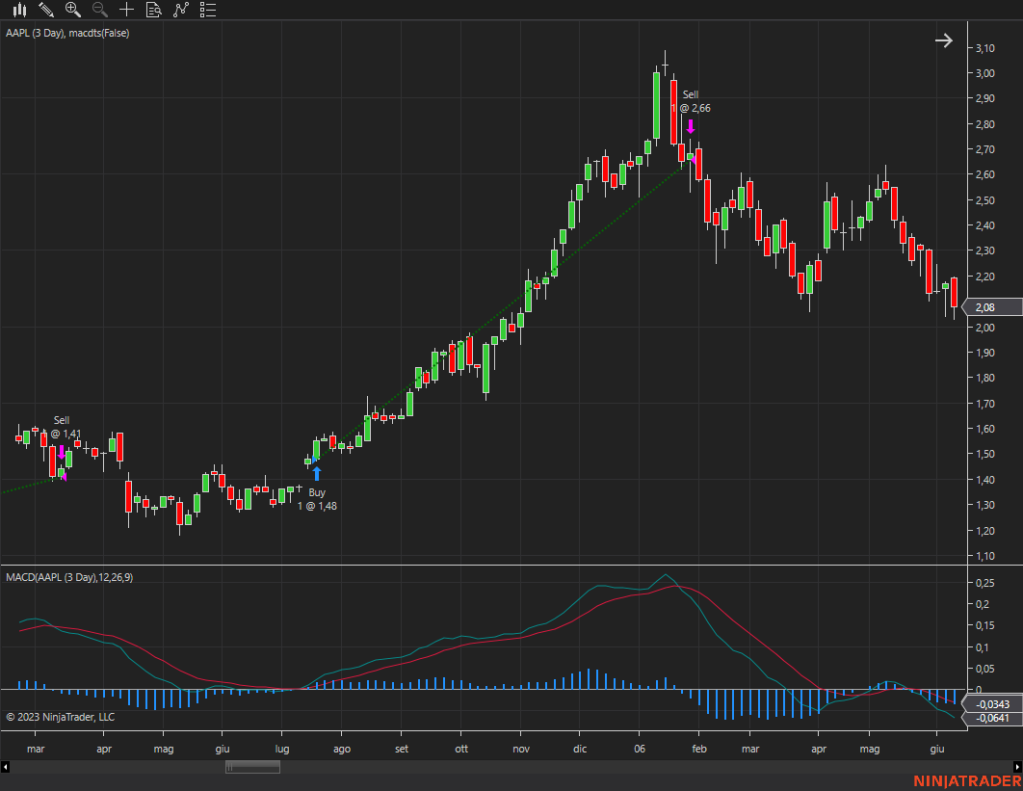
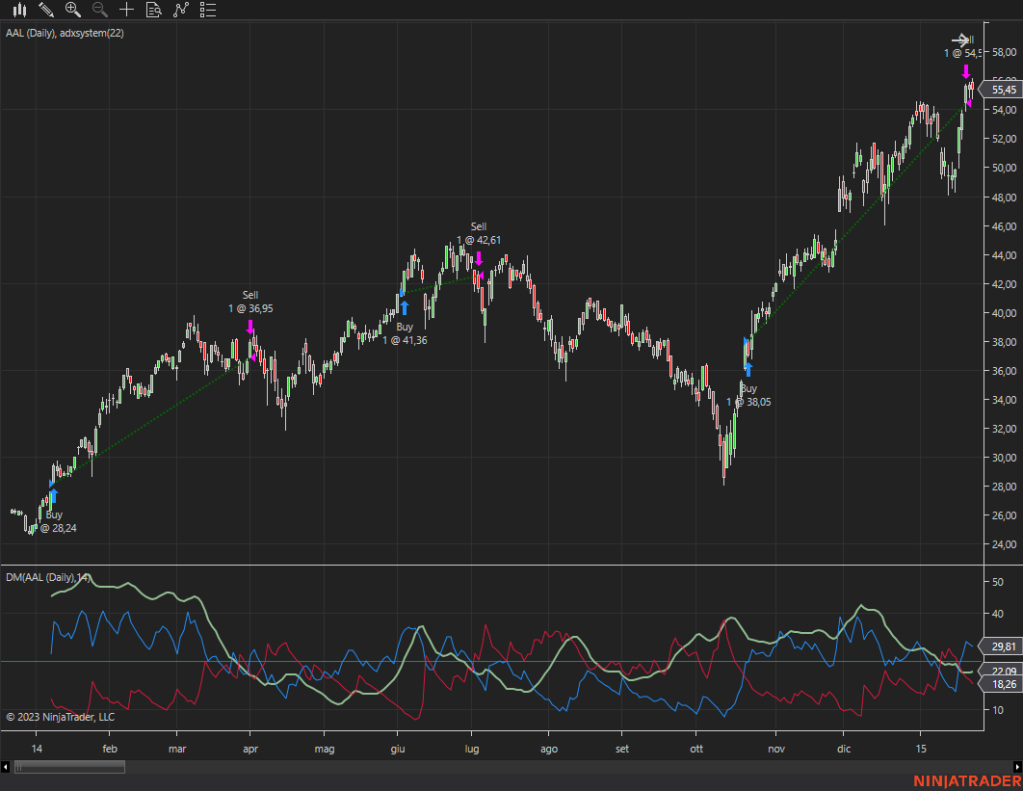
Trend-Following Strategies: Trend-following strategies exploit the empirical regularity of price momentum. These strategies aim to identify and capitalize on established trends in the market. Traders using trend-following strategies enter trades in the direction of the prevailing trend, riding the momentum until signs of reversal emerge. Common trend-following indicators include moving averages, trendlines, and momentum oscillators. By aligning their trades with the underlying market trend, traders can capture profits as prices continue to move in their favor.
Mean-Reversion Strategies: Mean-reversion strategies capitalize on the empirical regularity of prices reverting to their historical mean. These strategies identify periods of overbought or oversold conditions in the market and seek to profit from the subsequent price corrections. Mean-reversion traders typically look for deviations from the historical average, using indicators such as Bollinger Bands, RSI (Relative Strength Index), and stochastic oscillators to identify potential reversal points. By entering contrarian trades when prices deviate significantly from their mean, traders can capture profits as prices revert to their long-term equilibrium.
Challenges and Considerations
While empirical regularities offer valuable insights into market behavior, traders must approach them with caution and critical thinking. Market conditions are dynamic and subject to change, and what may have worked in the past may not necessarily hold true in the future. Overreliance on historical patterns without considering evolving market dynamics and fundamental factors can lead to suboptimal trading decisions and increased risk exposure.
Moreover, the proliferation of algorithmic trading and high-frequency trading strategies has led to shorter market cycles and increased market efficiency. This trend has made it increasingly challenging for traders to exploit traditional empirical regularities effectively. In such a competitive environment, traders must continuously adapt and innovate their strategies to remain profitable. This may involve incorporating alternative data sources, refining analytical techniques, or developing more sophisticated trading algorithms.
Conclusion
Empirical regularity represents a powerful tool for traders seeking to navigate the complexities of financial markets. By uncovering recurring patterns and relationships within historical data, traders can gain valuable insights into market dynamics and develop strategies that tilt the odds of success in their favor. However, it is essential to approach empirical regularities with a balanced perspective, recognizing their limitations and the ever-evolving nature of financial markets. By combining data-driven analysis with sound judgment and adaptability, traders can harness the power of empirical regularity to thrive in an increasingly competitive trading landscape. As traders continue to push the boundaries of innovation and technology, empirical regularity remains a timeless principle that underpins success in the world of trading.